Studies show that oats and oatmeal have many health benefits. These include weight loss, lower blood sugar levels, and a reduced risk of heart disease.
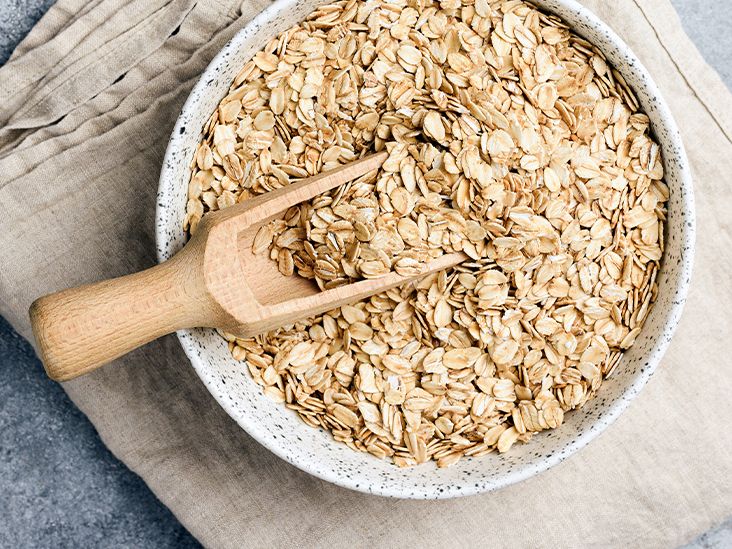
Oats are among the healthiest grains on earth. They’re a gluten-free whole grain and a great source of important vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants.
Here are 9 evidence-based health benefits of eating oats and oatmeal.
Oats are a whole grain food, known scientifically as Avena sativa.
The most intact and whole form of oats are oat groats, which take a long time to cook. For this reason, many people prefer rolled, crushed, or steel-cut oats.
Instant (quick) oats are the most highly processed variety. While they take the shortest time to cook, the texture may be mushy.
Oats are commonly eaten for breakfast as oatmeal, which is made by boiling oats in water or milk. Oatmeal is often referred to as porridge.
They’re also often included in muffins, granola bars, cookies, and other baked goods.
Summary
Oats are a whole grain commonly eaten for breakfast as oatmeal (porridge) and added to baked goods.
The nutrient composition of oats is well-balanced. They are a good source of carbs and fiber, including the fiber
Oats are also a good source of
Oats are loaded with important vitamins, minerals, and antioxidant plant compounds.
Half a cup (40.5 grams) of dry oats
The nutritional profile of one cup prepared oatmeal (one half cup dry oats with water) also includes:
- 25/5 grams of carbs
- 6.5 grams of protein
- 2.5 grams of fat
- 4 grams of fiber
- 151.5 calories
This means that oats are among the most nutrient-dense foods you can eat.
Summary
Oats are rich in carbs and fiber, but also higher in protein and fat than most other grains. They contain many vitamins and minerals.
Whole oats are high in antioxidants and beneficial plant compounds called polyphenols. Most notable is a unique group of antioxidants called
Research has found that avenanthramides may help lower blood pressure levels by increasing the production of nitric oxide gas. This gas molecule helps dilate (widen) blood vessels, which may lead to better blood flow.
In addition,
Summary
Oats contain many antioxidants, including avenanthramides. These compounds may help reduce blood pressure and have anti-inflammatory and anti-itching effects.
Oats contain large amounts of beta-glucan, a type of soluble fiber. Beta-glucan partially dissolves in water and forms a thick, gel-like solution in your gut.
The health benefits of beta-glucan fiber include:
Summary
Oats are high in the soluble fiber beta-glucan, which has numerous benefits. It helps reduce blood glucose levels, promotes healthy gut bacteria, and can regulate type 2 diabetes.
Many studies have shown that the beta-glucan fiber in oats is effective at reducing both total and LDL (bad) cholesterol levels.
Beta-glucan may increase the release of cholesterol-rich bile, which reduces the circulating levels of cholesterol in your blood.
Oats may also protect LDL (bad) cholesterol from oxidation.
Oxidation of LDL (bad) cholesterol occurs when it reacts with free radicals. This is another crucial step in the progression of heart disease.
LDL cholesterol produces inflammation in arteries, damages tissues, and can raise the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Summary
Oats may lower the risk of heart disease by reducing both total and LDL (bad) cholesterol, as well as by protecting LDL from oxidation.
Type 2 diabetes is a common health condition, characterized by significantly elevated blood sugar levels. It usually results from decreased sensitivity to the hormone insulin.
Oats may help lower blood sugar levels, especially in people with obesity or who have type 2 diabetes.
These effects are mainly attributed to beta-glucan’s ability to form a thick gel that delays the emptying of the stomach and absorption of glucose into the blood.
The beta-glucan in both oats and barley may also improve insulin sensitivity.
However, a randomized clinical trial in 2016 saw no improvement in insulin sensitivity, so further research is needed.
Summary
Due to the soluble fiber beta-glucan, oats may improve insulin sensitivity and help lower blood sugar levels.
Not only is oatmeal (porridge) a delicious breakfast food, but it’s also very filling. Eating filling foods
By delaying the time it takes your stomach to empty of food, the beta-glucan in oatmeal may increase your feeling of fullness.
Beta-glucan may also promote the release of peptide YY (PYY), a hormone produced in the gut in response to eating. This satiety hormone has been shown to lead to reduced calorie intake and may decrease your risk of obesity.
Summary
Oatmeal may help you lose weight by making you feel more full. It does this by slowing down the emptying of the stomach and increasing the production of the satiety hormone PYY.
It’s no coincidence that oats can be found in numerous skin care products. Makers of these products often label finely ground oats as “colloidal oatmeal.”
The FDA approved colloidal oatmeal as a skin-protective substance back in 2003. But oats have a long history of use in the
For example, oat-based skin products may improve uncomfortable symptoms of eczema.
Note that skin care benefits pertain only to oats applied to the skin, not those that are eaten.
Summary
Colloidal oatmeal (finely ground oats) has long been used to help treat dry and itchy skin. It may help relieve symptoms of various skin conditions, including eczema.
It’s an inflammatory disorder of the airways — the tubes that carry air to and from a person’s lungs.
Although not all children have the same symptoms, many experience recurrent coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath.
But whether oats can help prevent asthma development in children is still debated.
Summary
Some research suggests that oats may help prevent asthma in children when fed to young infants, but more research is still needed.
People of all ages and populations experience constipation. This refers to infrequent, irregular bowel movements that are difficult to pass.
Constipation affects nearly
Studies indicate that oat bran, the fiber-rich outer layer of the grain, may help relieve constipation.
Oat bran was also shown to decrease gastrointestinal symptoms and aid digestion in people living with ulcerative colitis (UC).
However, while the soluble fiber in oats is generally effective against constipation, it has been found to be less effective against opioid-induced constipation. This is because it doesn’t affect the movement of the colon that the drugs may suppress.
Summary
Studies indicate that oat bran can help relieve constipation and aid digestion in those living with gastrointestinal conditions like UC.
You can enjoy oats in several ways. The most popular way is to simply eat oatmeal (porridge) for breakfast.
Here is what you need to make oatmeal:
- 1/2 cup rolled oats
- 1 cup (250 ml) water or milk
- A pinch of salt
Combine ingredients in a pot and bring to a boil. Reduce heat to a simmer and cook the oats, stirring occasionally, until soft.
To make oatmeal tastier and even more nutritious, you can add cinnamon, fruits, nuts, seeds, and Greek yogurt.
Oats are often also included in baked goods, muesli, granola, and bread.
Although oats are naturally gluten-free, they are sometimes contaminated with gluten. That’s because they may be harvested and processed using the same equipment as other grains that contain gluten.
If you have celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, choose oat products that are certified as gluten-free.
Summary
Oats can be a great addition to a healthy diet and are naturally gluten-free. They can be eaten as oatmeal (porridge) for breakfast, added to baked goods, and more.
Is it healthy to eat oats every day?
In one study from 2020, the health of participants with inactive (quiescent) UC who ate oat bran daily for 24 weeks was maintained, and they did not experience their symptoms getting worse. This suggests oats can be consumed every day.
However, since oats are high in fiber, you may notice changes in your stool’s appearance and the frequency at which you poop.
Consuming an excess amount of oats may also lead to decreased nutrient absorption.
What’s the difference between wheat and oats?
The nutrient composition of oats and wheat is different, but both are good sources of protein, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals.
Minerals you can find in both wheat and oats at similar levels include magnesium, zinc, and iron.
Naked oats are highest in fats, while husked oats are highest in soluble fiber — but not total dietary fiber — compared with the cereal grains barley, rye, triticale, rice, and wheat.
Oats are a nutritious food packed with important vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. In addition, they’re higher in soluble fiber and protein compared to other grains.
Oats have unique components like the soluble fiber beta-glucan and antioxidants called avenanthramides.
Benefits include lower blood sugar and cholesterol levels, protection against skin irritation, and reduced constipation.
In addition, they are very filling, can be enjoyed several ways, and have many properties that should make them a food helpful for weight loss.
At the end of the day, oats are among the most nutrient-dense foods you can eat.
 skyglide Explore Beyond
skyglide Explore Beyond